Hip

Coxarthrosis (Hip Joint Arthrosis)
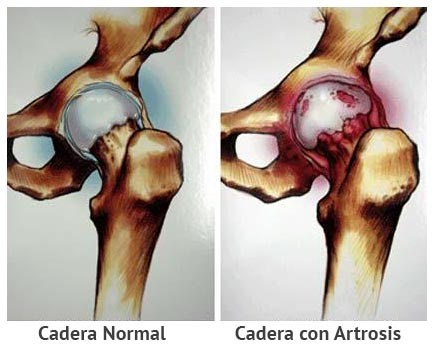
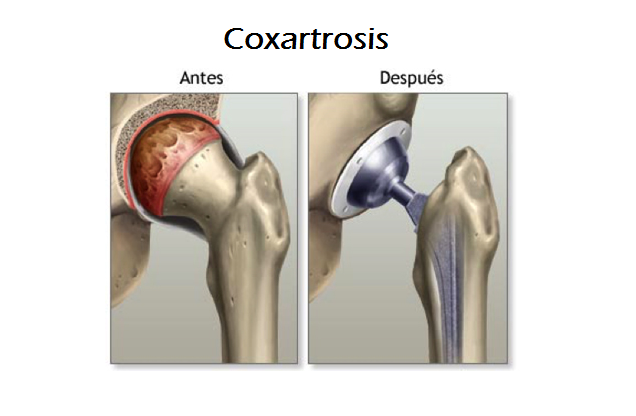
The most common cause of ailments in the hip joint is cartilage wear (osteoarthritis). In most cases it is atrophy, due to age, of the cartilaginous layer. However, diseases such as rheumatism, positional failures or deformations of the head of the femur or the acetabular cavity can also cause coccal osteoarthritis. Patients complain of increasing pain in the groin and / or thigh region. Increasing stiffness of the hip joint occurs, generally associated with disturbances of rest or stress. The radiograph shows a decrease in the inter-articular space and the formation of bony adhesions. Due to the associated discomfort and the failure of traditional therapies, the only viable alternative is usually the implantation of an artificial joint (total endoprosthesis). The prosthesis is a replica of the natural hip joint, including the head and socket. Generally, a ceramic head is combined with a polyethylene cavity. Using a design sketch, the action gauge and cavity size are determined for each patient prior to surgery. The prosthesis is designed according to the patient’s age, anatomical conditions and body weight. Several components are available.

Coxarthrosis (Hip Joint Arthrosis)
The most common cause of ailments in the hip joint is cartilage wear (osteoarthritis). In most cases it is atrophy, due to age, of the cartilaginous layer. However, diseases such as rheumatism, positional failures or deformations of the head of the femur or the acetabular cavity can also cause coccal osteoarthritis. Patients complain of increasing pain in the groin and / or thigh region. Increasing stiffness of the hip joint occurs, generally associated with disturbances of rest or stress. The radiograph shows a decrease in the inter-articular space and the formation of bony adhesions. Due to the associated discomfort and the failure of traditional therapies, the only viable alternative is usually the implantation of an artificial joint (total endoprosthesis). The prosthesis is a replica of the natural hip joint, including the head and socket. Generally, a ceramic head is combined with a polyethylene cavity. Using a design sketch, the action gauge and cavity size are determined for each patient prior to surgery. The prosthesis is designed according to the patient’s age, anatomical conditions and body weight. Several components are available.
For absorption into the bone, both the socket and the stem are specially coated. The two components are inserted into the bone under pressure. Cementless prostheses are particularly recommended for “young” and active patients.
Stem and socket anchoring is done by using bone cement.
Fixation of the cavity is done without cement (under pressure), the stem is fixed in the femur with cement. For the component parts of the joint, that is to say head and socket, different materials can be chosen, which are distinguished by their behavior under friction.
The parts in direct contact are made of polyethylene, ceramic material or metal.
On average, the durability of a hip replacement is usually 10 to 15 years. Joint implant surgeries can only be performed stationary (approx. 10-14 days). Right away, most patients are referred to a rehab clinic for 3 to 4 weeks. After this follows a period of outpatient rehabilitation lasting 2 to 3 months. With a normal development of the operation and a successful rehabilitation, patients will be able to exercise without problems certain sports, such as cycling, swimming, golf or walking. Some patients can even exercise sports like tennis or skiing. However, this is generally not recommended.
The parts in direct contact are made of polyethylene, ceramic material or metal.
On average, the durability of a hip replacement is usually 10 to 15 years. Joint implant surgeries can only be performed stationary (approx. 10-14 days). Right away, most patients are referred to a rehab clinic for 3 to 4 weeks. After this follows a period of outpatient rehabilitation lasting 2 to 3 months. With a normal development of the operation and a successful rehabilitation, patients will be able to exercise without problems certain sports, such as cycling, swimming, golf or walking. Some patients can even exercise sports like tennis or skiing. However, this is generally not recommended.

